Embark on a journey into the realm of cybersecurity best practices, where the stakes are high and the need for vigilance paramount. Recent cyber threats loom large, underlining the critical nature of implementing robust security measures. From password policies to network infrastructure, every facet plays a crucial role in fortifying defenses against malicious actors.
Join us as we delve into the world of cybersecurity best practices and uncover the key strategies for safeguarding your digital assets.
Importance of Cybersecurity Best Practices
In today's digital age, cybersecurity best practices are more crucial than ever for organizations to protect their sensitive data and maintain the trust of their customers. By implementing robust cybersecurity measures, businesses can safeguard against a wide range of cyber threats and breaches.
Recent Cyber Threats and Breaches
In recent years, we have witnessed a surge in cyber attacks targeting organizations of all sizes and industries. One notable example is the ransomware attack on Colonial Pipeline in 2021, which disrupted fuel supplies along the East Coast of the United States.
This incident highlighted the devastating impact of cyber threats on critical infrastructure and the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures.
- Another significant breach was the SolarWinds cyber attack in 2020, where hackers compromised the software supply chain to infiltrate multiple government agencies and corporations. This breach underscored the need for organizations to strengthen their cybersecurity defenses and enhance threat detection capabilities.
- The Equifax data breach in 2017 exposed the personal information of millions of individuals, leading to widespread financial fraud and identity theft. This incident demonstrated the severe consequences of failing to implement adequate cybersecurity best practices.
Potential Consequences of Ineffective Cybersecurity Practices
Failure to implement cybersecurity best practices effectively can have devastating consequences for organizations, including:
- Data Breaches:Exposing sensitive information such as customer data, intellectual property, and financial records can result in reputational damage and legal repercussions.
- Financial Loss:Cyber attacks can lead to financial losses through ransom payments, regulatory fines, and operational disruptions.
- Disruption of Services:Downtime caused by cyber incidents can impact business operations, customer trust, and overall productivity.
- Legal Consequences:Non-compliance with data protection regulations can lead to costly legal penalties and lawsuits.
Key Components of Cybersecurity Best Practices
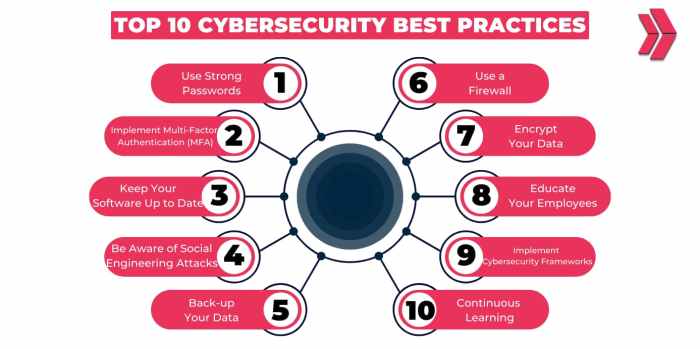
Implementing a robust cybersecurity strategy involves various key components that work together to protect sensitive data and systems from cyber threats.
Essential Elements of a Robust Cybersecurity Strategy
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting routine audits to identify vulnerabilities and assess the overall security posture of the organization.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforcing complex password requirements and implementing multi-factor authentication to enhance access control.
- Network Security Measures: Deploying firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols to safeguard network infrastructure.
- Incident Response Plan: Developing a detailed plan to effectively respond to and mitigate cybersecurity incidents when they occur.
Role of Employee Training in Maintaining Cybersecurity Best Practices
- Security Awareness Training: Educating employees on cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing emails and avoiding social engineering attacks.
- Policy Compliance: Ensuring employees adhere to security policies and procedures to minimize human errors that could lead to security breaches.
- Continuous Learning: Providing ongoing training to keep employees informed about the latest cyber threats and mitigation strategies.
Tools and Technologies to Enhance Cybersecurity Best Practices
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Implementing antivirus software, endpoint detection and response tools to protect endpoints from malware and cyber threats.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: Monitoring and analyzing security events in real-time to detect and respond to suspicious activities.
- Vulnerability Scanning Tools: Conducting regular scans to identify weaknesses in systems and applications that could be exploited by attackers.
Implementing Strong Password Policies
When it comes to cybersecurity, implementing strong password policies is crucial in protecting sensitive information and preventing unauthorized access. Strong passwords can act as the first line of defense against cyber threats.
Design Guidelines for Creating Secure Passwords
- Use a combination of letters (both uppercase and lowercase), numbers, and special characters.
- Avoid using easily guessable information such as birthdays, names, or words found in the dictionary.
- Create passwords that are at least 12-16 characters long to increase complexity.
- Consider using passphrases that are easy for you to remember but difficult for others to guess.
Importance of Using Multi-Factor Authentication Along with Passwords
Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more forms of verification before granting access. This could include something you know (password), something you have (security token), or something you are (fingerprint).
Examples of Password Management Tools
- LastPass:A popular password manager that securely stores all your passwords in one place.
- 1Password:Another reliable password manager that offers features like password generation and secure sharing.
- Dashlane:A user-friendly password manager with a built-in VPN for added security.
Securing Network Infrastructure
Securing network infrastructure is crucial to maintaining the overall cybersecurity of an organization. By implementing methods to protect network devices and data transmission, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats and attacks.
One key concept in securing network infrastructure is network segmentation. This involves dividing a network into smaller subnetworks to limit the spread of potential threats. By segmenting the network, organizations can contain any security breaches and prevent them from affecting the entire system.
Network Segmentation
- Implementing firewalls to separate network segments and control traffic flow.
- Using VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) to isolate different parts of the network.
- Restricting access to sensitive data by creating separate segments for critical assets.
Monitoring and Managing Network Traffic
- Utilizing intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to detect and prevent unauthorized access.
- Setting up network monitoring tools to track network activity and identify any anomalies or suspicious behavior.
- Regularly reviewing logs and alerts to stay informed about potential security incidents.
Regular Software Updates and Patch Management
Regular software updates and patch management are crucial aspects of cybersecurity best practices. By ensuring that software is up to date with the latest security patches, organizations can mitigate vulnerabilities and reduce the risk of cyber attacks.
Significance of Timely Software Updates and Patches
Regular software updates and patches are essential for addressing newly discovered security vulnerabilities. Hackers are constantly looking for ways to exploit weaknesses in software, and by keeping systems updated, organizations can stay ahead of potential threats.
Challenges and Solutions in Patch Management
One of the challenges in patch management is the complexity of managing updates across multiple devices and systems. To overcome this, organizations can implement patch management tools that automate the deployment of patches and ensure that all systems are up to date.
Tools and Strategies for Automating Software Updates
- Utilize patch management software such as Microsoft SCCM or WSUS to automate the deployment of patches across networks.
- Implement automated vulnerability scanning tools like Nessus or Qualys to identify missing patches and prioritize updates based on risk.
- Consider using endpoint protection platforms that include built-in patch management capabilities to streamline the update process.
Ending Remarks
As our exploration of cybersecurity best practices comes to a close, one thing is clear: proactive measures are the cornerstone of a secure digital environment. By adhering to the principles Artikeld, organizations can effectively mitigate risks and protect their valuable assets from potential threats.
Stay informed, stay vigilant, and stay secure in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity.
Clarifying Questions
How often should passwords be changed?
Passwords should ideally be changed every 90 days to maintain security.
What is the role of encryption in cybersecurity?
Encryption plays a vital role in protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access by converting it into a secure format.
Why is employee training crucial for cybersecurity?
Employee training is essential to ensure that staff are aware of security best practices and can identify potential threats.
What are the benefits of network segmentation?
Network segmentation helps in containing breaches and limiting the impact of cyber attacks by isolating different parts of the network.
How can software update automation improve cybersecurity?
Automating software updates ensures that systems are regularly patched, reducing vulnerabilities and enhancing overall security.








